Balanced scorecard: the fourfold approach to strategic success
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management tool that aligns management and employees in four perspectives on an organization’s vision and strategy. This article outlines the perspectives, benefits, and implementation of the balanced scorecard.
What is a balanced scorecard?
To understand the concept of the balanced scorecard (BSC), it is important to understand what a scorecard is. In business, it describes a statistical record that is used to track progress or performance toward a certain objective. The basic principle of the BSC is that an organization pursues a vision and a strategy aligned to it. It uses four perspectives on that vision and strategy, which are presented in targets, methods, and ratios.
Benefits of the balanced scorecard
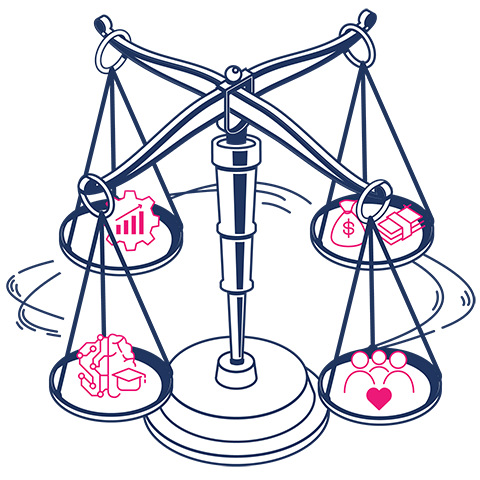
The BSC offers a more holistic approach than the simple scorecard. It takes four perspectives into account: the customer perspective, the internal perspective, the innovation and learning perspective, and the financial perspective. Therefore, it is called “balanced.” Specific questions are asked for each perspective:
- The customer perspective: how do our customers see us and what are their needs?
- The internal perspective: what do we need to excel in? How can internal processes help reach our customers’ goals?
- The innovation and learning perspective: how do we continuously create and improve value? How can we empower and motivate our employees to deliver on objectives?
- The financial perspective: what can we give our investors?
When using the BSC approach, it is necessary to understand that all four perspectives are weighted equally in a cause-effect relationship. Skilled and motivated employees are crucial for the overall organizational performance. Efficient and effective processes allow employees to deliver on goals, the customer perspective is required for financial success, and so on. Combining all four perspectives allows for a comprehensive overview for both management and employees. It enables a better understanding of entrepreneurial success and failure.
Furthermore, the BSC approach minimizes information overload by limiting the number of measures used. It compels management to focus on the most critical measures, since organizations rarely deal with too little information.
Historical background of the balanced scorecard
The concept of the BSC was developed by economist Robert S. Kaplan and economic theorist David P. Norton in the early 1990s. The conceptual basis was the transformation of strategies into actions. Since then, the BSC has been used as a measurement tool for entrepreneurial activities by organizations, nonprofit organizations, governments, and others.
Implementing the balanced scorecard
The higher the influence of external factors on an organization, the greater the importance of drafting a vision and strategy. Organizations must stay adaptable to different scenarios to stay competitive and successful. It is crucial to develop a strategic plan that accounts for changing circumstances and considers both management and employees.
To make the strategy feasible, the BSC is divided into goals, target values, and measures:
- The first step is drafting the vision.
- This is also the first goal from which further subgoals are derived in the second step.
- In the third step, for each of the four perspectives, key objectives and subgoals with respective key figures and metrics are defined.
- The final step is to define actions that need to be taken to reach the target values, and incorporate these into the reporting system.
When working with the BSC, it is important to use it as an adaptable planning instrument that accounts for constant internal and external changes. The BSC is continuously adjusted.
Conclusion: how to effectively use the balanced scorecard
The BSC is a strategic guide for the future of a company, not a mere key performance indicator. When using this management approach, it is important to understand that communication is the central factor of success. The involvement of all employees in reaching the organizational goals creates transparency. This in turn enables a good orientation and positioning for everyone, and ultimately leads to collective success.